[Note] Mạng neural và mạng tích chập: Khái niệm và ứng dụng
Published:
Khái niệm và ứng dụng của mạng neural và mạng tích chập
Mạng neuron nhân tạo và ứng dụng
Các khái niệm cơ bản
- Tìm hiểu về kiến trúc và cách cài đặt mạng neuron
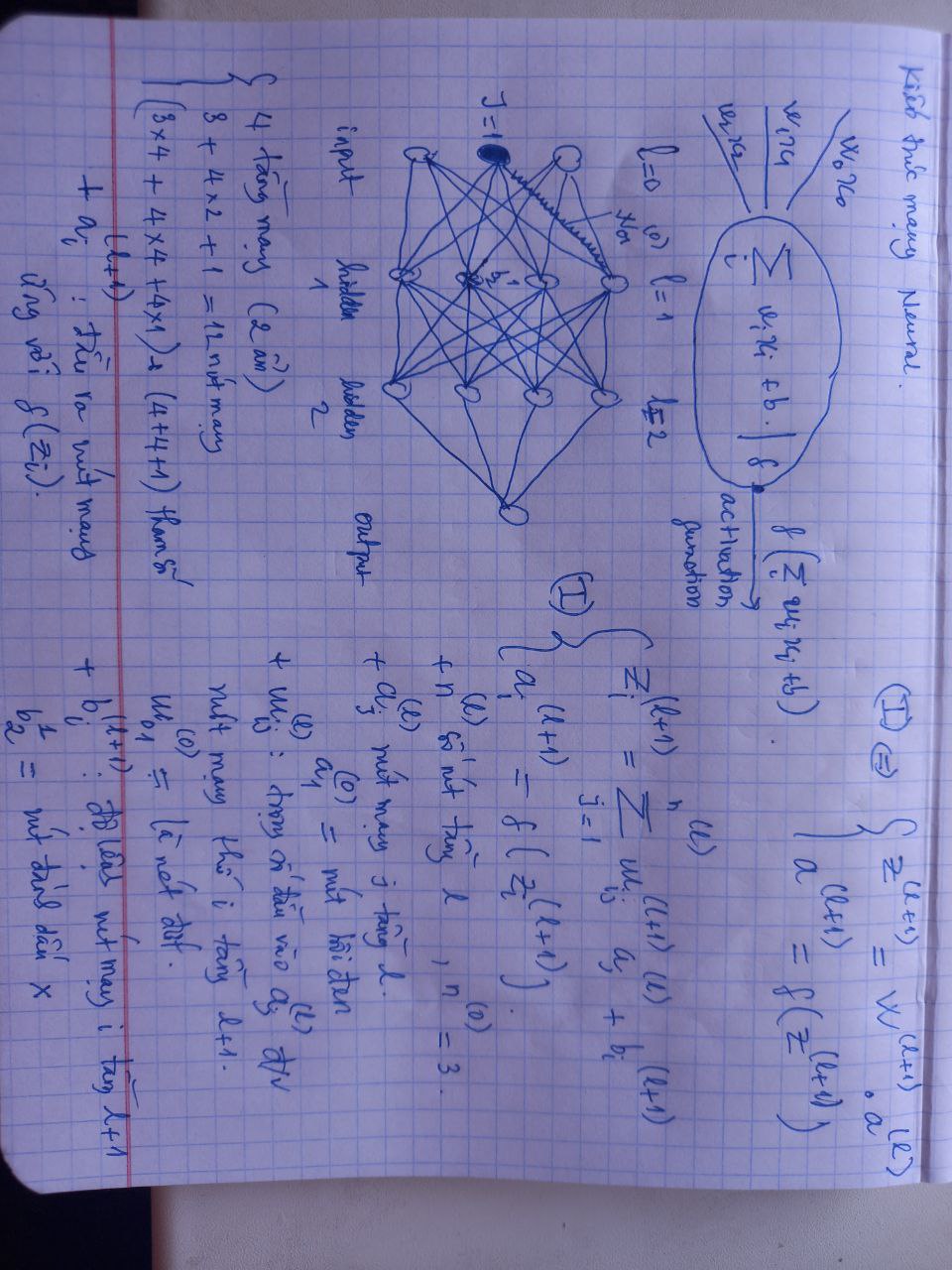
Kiến trúc mạng neuron
- Giới thiệu kiến trúc và ký hiệu của mạng neuron
Cách tính đạo hàm tiến (feedforward) và lan truyền ngược (back propagation)
- Công thức tính đạo hàm tiến và cách thực hiện lan truyền ngược

Hàm lỗi và chứng minh đạo hàm
- Hàm lỗi và chứng minh chi tiết đạo hàm của lan truyền ngược

Ứng dụng vào bài toán MNIST
- Ứng dụng mạng neural vào bài toán phân lớp dựa vào tập dữ liệu MNIST
Load dữ liệu của bài toán
import os
import gzip
import pickle
import numpy as np
import urllib3
DATA_FILE = 'mnist.pkl.gz'
def download():
# download MNIST dataset
url = 'https://github.com/mnielsen/neural-networks-and-deep-learning/raw/master/data/mnist.pkl.gz'
http = urllib3.PoolManager()
r = http.request('GET', url, preload_content = False)
with open(DATA_FILE, 'wb') as out:
while True:
data = r.read(4096)
if not data:
break
out.write(data)
r.release_conn()
print('downloaded!')
# one hot label [1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10]
# chuyen thanh vector nhi phan tai position = 1
def label_2_vec(label):
v = np.zeros((10, 1))
v[label] = 1.0
return v
def load():
if not os.path.exists(DATA_FILE):
download()
with gzip.open(DATA_FILE, 'rb') as file:
tr_dt, v_dt, t_dt = pickle.load(file, encoding='iso-8859-1')
# training data
inputs = [x.reshape((784, 1)) for x in tr_dt[0]]
labels = [label_2_vec(y) for y in tr_dt[1]]
training_data = zip(inputs, labels)
# validataion data
inputs = [x.reshape((784, 1)) for x in v_dt[0]]
validation_data = zip(inputs, v_dt[1])
# test data
inputs = [x.reshape((784, 1)) for x in t_dt[0]]
test_data = zip(inputs, t_dt[1])
return (training_data, validation_data, test_data)
Đọc dữ liệu và kiếm tra việc sinh ma trận trọng số (w)
training_data, validation_data, test_data = load()
training_data = list(training_data)
validataion_data = list(validation_data)
test_data = list(test_data)
# test sinh ma tran w
layers = [784, 100, 200, 10]
for l2, l1 in zip(layers[1:], layers[:-1]):
print(l2, l1)
Xây dựng class Mạng neural
import time
import random
class NN():
def __init__(self, layers):
# layers = [784, 100, 200, 10]
self.layers = layers
self.L = len(layers)
self.w = [np.random.randn(l2, l1 + 1) for l2, l1 in zip(layers[1:], layers[:-1])]
#w[0] = (100, 785), 1 cot la bias
#w[1] = (200, 101) # trong so doi voi tang 2
#w[2] = (10, 201) # trong so doi voi tang 3
def feedforward(self, x): #x: 1 buc anh.
z = []
a = [self.add_bias(x)] # a0 = x
for l in range(1, self.L):
#l = [0, 1, 2, 3]
#w[0] la trong so doi voi tang 1
z_l = np.dot(self.w[l-1], a[l-1])
a_l = self.sigmoid(z_l)
if l < self.L - 1:
a_l = self.add_bias(a_l) # add bias doi voi tang (khac cuoi cung)
z.append(z_l)
a.append(a_l)
return (z, a)
def predict(self, x):
_, a = self.feedforward(x)
return np.argmax(a[-1])
def add_bias(self, a):
# a = [784, 1]
# after add_bias --> [785, 1] voi a[0] = 1
return np.insert(a, 0, 1, axis = 0)
def sigmoid(self, z):
# sigmoid function use as activation function
return 1.0 / (1.0 + np.exp(-z))
def cost(self, data):
# return cross-entropy cost of NN on test data
m = len(data)
j = 0
for x, y in data:
# x: (784, 1)
# y: label (ex: 7)
_, a = self.feedforward(x)
a_L = a[-1]
j += np.sum(np.nan_to_num(y * np.log(a_L) + (1 - y) * np.log(1 - a_L)))
return -j / m
def evaluate(self, test_data):
results = [(self.predict(x), y) for (x, y) in test_data]
return sum(int(_y == y) for (_y, y) in results)
def backprop(self, x, y):
# backpropagation to calc derivatives
w_grad = [np.zeros(W.shape) for W in self.w]
#feedforward
z, a = self.feedforward(x)
#backward
dz = a[-1] - y # da chung minh o hinh viet.
for _l in range(1, self.L):
l = -_l # layer index
if l < -1:
#da = a[l] * (1 - a[l])
da = self.sigmoid_grad(z[l])
# do not calc for w_0 (da_0 /dz = 0 because a_0 = 1 for all z)
dz = np.dot(self.w[l+1][:, 1:].transpose(), dz) * da
# gradient
w_grad[l] = np.dot(dz, a[l-1].transpose())
return w_grad
def sigmoid_grad(self, z):
s = self.sigmoid(z)
return s * (1 - s)
def train(self, train_data, epochs, mini_batch_size, eta):
# train NN with train data
# use mini-batch SGD method to train the NN
m = len(train_data)
# cost
cost = []
for j in range(epochs):
start_time = time.time()
#shuffle data before run
random.shuffle(train_data)
#divide data into mini batchs
for k in range(0, m, mini_batch_size):
mini_batch = train_data[k : k + mini_batch_size]
m_batch = len(mini_batch)
# calc gradient
w_grad = [np.zeros(W.shape) for W in self.w]
for x, y in mini_batch:
grad = self.backprop(x, y)
w_grad = [W_grad + g for W_grad, g in zip(w_grad, grad)]
w_grad = [W_grad / m_batch for W_grad in w_grad]
#update w
self.w = [W - eta * W_grad for W, W_grad in zip(self.w, w_grad)]
# calc cost
cost.append(self.cost(train_data))
return cost
Test và đánh giá mô hình
- Sử dụng 1 lớp ẩn
nn = NN([784, 100, 10])
nn.train(training_data, 30, 100, 3.0)
correct = nn.evaluate(test_data)
total = len(test_data)
print(correct, total, 100.0 * correct / total)
- Hoặc sử dụng 2 lớp ẩn
nn = NN([784, 100, 200, 10])
nn.train(training_data, 30, 100, 3.0)
correct = nn.evaluate(test_data)
total = len(test_data)
print(correct, total, 100.0 * correct / total)
Giải thích cơ chế của mạng neural networks
- Bước 1

- Bước 2
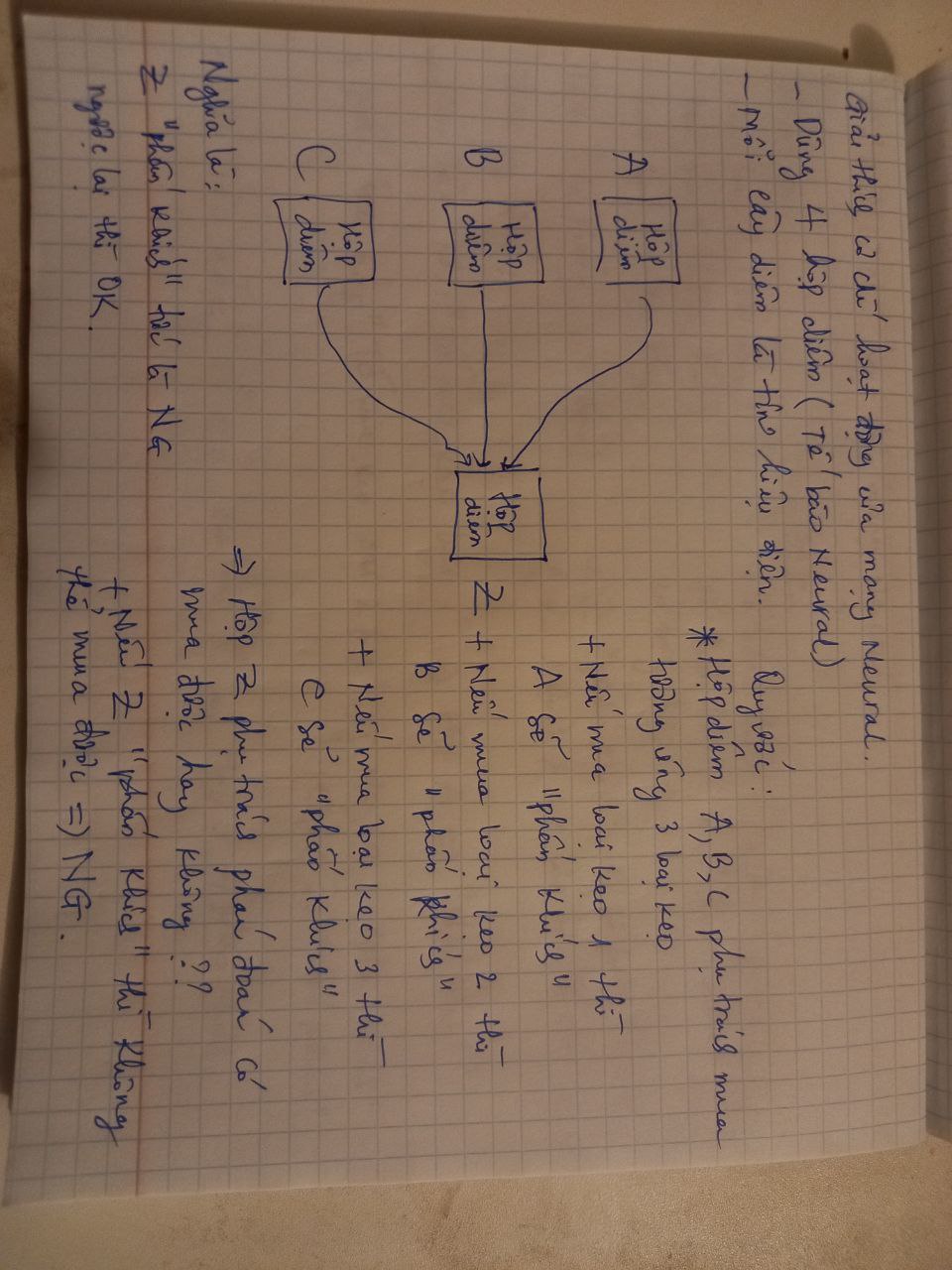
- Bước 3

- Bước 4

- Bước 5

- Bước 6

- Bước 7

Mạng tích chập neural
Convolution & Correlation
- Tìm hiểu về kiến trúc và cách cài đặt mạng tích chập neural
- Giới thiệu phép tích chập và phép correlation

Convolution Layer - Forward
- Giới thiệu công thức tính forward

Khởi tạo Convolution
- Giải thích và cài đặt
import numpy as np
from scipy import signal
from layer import Layer
class Convolutional(Layer):
# Tinh forward va backward cho lop Convolutional
def __init__(self, input_shape, kernel_size, depth):
input_depth, input_height, input_width = input_shape # (inputshape (m, h, w)
# input_depth: so luong input dau vao (m: size)
# depth: nume_layer_kernel
self.depth = depth
self.input_shape = input_shape
self.input_depth = input_depth
self.output_shape = (depth, input_height - kernel_size + 1, input_width - kernel_size + 1)
self.kernels_shape = (depth, input_depth, kernel_size, kernel_size)
#output_shape (num_layer_kernel, h - size_kernel + 1, w - size_kernel + 1)
#kernel_shape (num_layer_kernel, m, kernel_size, kernel_size)
#kernels (dua tren kernels_shape
self.kernels = np.random.randn(*self.kernels_shape)
#biases (dua tren size output_shape)
self.biases = np.random.randn(*self.output_shape)
def forward(self, input): # input * kernel + bias
# duyet tu num_layer_kernel, duyet cac input dulieu
# tinh tung output[i] (tu dau den cuoi)
self.input = input
self.output = np.copy(self.biases)
for i in range(self.depth):
for j in range(self.input_depth):
self.output[i] += signal.correlate2d(self.input[j], self.kernels[i, j], "valid")
return self.output
# dau vao: output_gradient, learning
# cach tinh da duoc giai thich o cac hinh (back_ward1,2,3,4)
def backward(self, output_gradient, learning_rate):
kernels_gradient = np.zeros(self.kernels_shape)
input_gradient = np.zeros(self.input_shape)
for i in range(self.depth):
for j in range(self.input_depth):
kernels_gradient[i, j] = signal.correlate2d(self.input[j], output_gradient[i], "valid")
input_gradient[j] += signal.convolve2d(output_gradient[i], self.kernels[i, j], "full")
self.kernels -= learning_rate * kernels_gradient
self.biases -= learning_rate * output_gradient
return input_gradient

Hàm lỗi và đạo hàm
- Cách tính hàm lỗi và đạo hàm
import numpy as np
# Do loi mse (binh phuong do lech)
def mse(y_true, y_pred):
return np.mean(np.power(y_true - y_pred, 2))
# Dao ham cua mse giua (y_true vs y_pred)
def mse_prime(y_true, y_pred):
return 2 * (y_pred - y_true) / np.size(y_true)
# Gia tri cua ham loi giua y_true vs y_pred (predict)
def binary_cross_entropy(y_true, y_pred):
return np.mean(-y_true * np.log(y_pred) - (1 - y_true) * np.log(1 - y_pred))
# Dao ham cua ham loi giua y_true va y_predict
def binary_cross_entropy_prime(y_true, y_pred):
return ((1 - y_true) / (1 - y_pred) - y_true / y_pred) / np.size(y_true)

Phương pháp backward (đối với convolution)
- Giải thích dạng toán học và cài đặt
def backward(self, output_gradient, learning_rate):
kernels_gradient = np.zeros(self.kernels_shape)
input_gradient = np.zeros(self.input_shape)
for i in range(self.depth):
for j in range(self.input_depth):
kernels_gradient[i, j] = signal.correlate2d(self.input[j], output_gradient[i], "valid")
input_gradient[j] += signal.convolve2d(output_gradient[i], self.kernels[i, j], "full")
self.kernels -= learning_rate * kernels_gradient
self.biases -= learning_rate * output_gradient
return input_gradient
- Backward 01

- Backward 02

- Backward 03

- Backward 04

Cài đặt đầy đủ CNN (cài từ đầu)
Class Layer (base)
# Lop base (Layer) gom co input, output
# method forward (input) --> "dao ham tien"
# method backward (output_gradient, learning rate) --> "dao ham nguoc"
# Cac lop ke thua lop (Layer) phai dinh nghia lai forward va backward
class Layer:
def __init__(self):
self.input = None
self.output = None
def forward(self, input):
# TODO: return output
pass
def backward(self, output_gradient, learning_rate):
# TODO: update parameters and return input gradient
pass
Hàm Activations
- Cài đặt các hàm activation
import numpy as np
from layer import Layer
# Lop Activation (ke thua Layer)
# Activation (actionvation function, activation prime - dao ham)
class Activation(Layer):
def __init__(self, activation, activation_prime):
self.activation = activation #ham activation
self.activation_prime = activation_prime # dao ham cua ham activation tuong ung.
# Khi forward no se call ham activation cho input dua vao
def forward(self, input):
self.input = input
return self.activation(self.input)
# Khi backward no thuc hien phep mul giua output_gradient vs activation_prime cua input
def backward(self, output_gradient, learning_rate):
return np.multiply(output_gradient, self.activation_prime(self.input))
- Cài đặt 2 hàm actionvation: Tanh, Sigmoid
import numpy as np
from layer import Layer
from activation import Activation
# Ham Tanh va sigmoid (2 ham nay la ham activation)
# Ham Tanh (ke thua Lop Activation)
# Dinh nghia ham Tanh va dao ham cua ham Tanh tuong ung
class Tanh(Activation):
def __init__(self):
def tanh(x):
return np.tanh(x)
def tanh_prime(x):
return 1 - np.tanh(x) ** 2
super().__init__(tanh, tanh_prime)
# Dinh nghia ham sigmoid va dao ham cua ham sigmoid
class Sigmoid(Activation):
def __init__(self):
def sigmoid(x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
def sigmoid_prime(x):
s = sigmoid(x)
return s * (1 - s)
super().__init__(sigmoid, sigmoid_prime)
# Lop softmax ke thua tu lop (Layer)
# Dinh nghia lai ham forward vs backward
# Softmax la mot Layer (no can duoc dinh nghia forward va backward)
class Softmax(Layer):
# forward: x^e / sum (x^e)
def forward(self, input):
tmp = np.exp(input)
self.output = tmp / np.sum(tmp)
return self.output
# Day la cong thuc tinh backward theo softmax
def backward(self, output_gradient, learning_rate):
# This version is faster than the one presented in the video
n = np.size(self.output)
return np.dot((np.identity(n) - self.output.T) * self.output, output_gradient)
# Original formula:
# tmp = np.tile(self.output, n)
# return np.dot(tmp * (np.identity(n) - np.transpose(tmp)), output_gradient)
Util Reshape.py
import numpy as np
from layer import Layer
# Reshape (no cung la mot Layer), can dinh nghia la forward vs backward
class Reshape(Layer):
# input cua Reshape la (input_shape, output_shape)
def __init__(self, input_shape, output_shape):
self.input_shape = input_shape
self.output_shape = output_shape
# qua trinh forward (input) --> reshape input theo (output_shape)
def forward(self, input):
return np.reshape(input, self.output_shape)
# qua trinh backward --> no reshape output_gradient theo dang (input_shape)
def backward(self, output_gradient, learning_rate):
return np.reshape(output_gradient, self.input_shape)
Lớp Dense
import numpy as np
from layer import Layer
# Lop Dense cung la mot Layer
class Dense(Layer):
# ham khoi tao (input_sie, vs output_size)
# --> sinh ra weights (output_size, input_size)
# --> bias (output_size, 1)
def __init__(self, input_size, output_size):
self.weights = np.random.randn(output_size, input_size)
self.bias = np.random.randn(output_size, 1)
# forward: tinh tich "dot" cua weights vs input + bias
def forward(self, input):
self.input = input
return np.dot(self.weights, self.input) + self.bias
# backward: tim lai input_gradient
# du lieu dau vao (output_gradient, learning_rate)
# cap nhat weigths vs bias (nguoc dau voi dao ham)
def backward(self, output_gradient, learning_rate):
# gradient cua weigths chinh la tich "dot" output_gradient vs intput.T
weights_gradient = np.dot(output_gradient, self.input.T)
# input_gradient chinh la tich "dot" cua weights.T vs output_gradient
input_gradient = np.dot(self.weights.T, output_gradient)
# cap nhat weights vs bias
self.weights -= learning_rate * weights_gradient
self.bias -= learning_rate * output_gradient
return input_gradient
Cài đặt network
- Cài đặt phương thức train và predict
def predict(network, input):
# input: dau vao de predict
# network: mang da co.
output = input
# duyet qua tung layer --> tinh forward den cuoi cung
# --> output tuong ung voi input dau vao.
for layer in network:
output = layer.forward(output)
return output
def train(network, loss, loss_prime, x_train, y_train, epochs = 1000, learning_rate = 0.01, verbose = True):
# duyet tu epochs
for e in range(epochs):
error = 0
# moi epochs tinh lai error
# duyet toan bo tap train
for x, y in zip(x_train, y_train):
# forward
output = predict(network, x)
# error
error += loss(y, output)
# backward
grad = loss_prime(y, output)
# duyet nguoc netork, tinh backward voi gradient_output (tinh theo ham loss vs loss_prime dua vao)
for layer in reversed(network):
grad = layer.backward(grad, learning_rate)
error /= len(x_train)
if verbose:
print(f"{e + 1}/{epochs}, error={error}")
Hàm Chính
import os
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '3'
import numpy as np
from keras.datasets import mnist
from keras.utils import np_utils
from dense import Dense
from convolutional import Convolutional
from reshape import Reshape
from activations import Sigmoid
from losses import binary_cross_entropy, binary_cross_entropy_prime
from network import train, predict
def preprocess_data(x, y, limit):
zero_index = np.where(y == 0)[0][:limit]
one_index = np.where(y == 1)[0][:limit]
all_indices = np.hstack((zero_index, one_index))
all_indices = np.random.permutation(all_indices)
x, y = x[all_indices], y[all_indices]
x = x.reshape(len(x), 1, 28, 28)
x = x.astype("float32") / 255
y = np_utils.to_categorical(y)
y = y.reshape(len(y), 2, 1)
return x, y
# load MNIST from server, limit to 100 images per class since we're not training on GPU
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()
x_train, y_train = preprocess_data(x_train, y_train, 100)
x_test, y_test = preprocess_data(x_test, y_test, 100)
# neural network
network = [
Convolutional((1, 28, 28), 3, 5),
Sigmoid(),
Reshape((5, 26, 26), (5 * 26 * 26, 1)),
Dense(5 * 26 * 26, 100),
Sigmoid(),
Dense(100, 2),
Sigmoid()
]
# train
train(
network,
binary_cross_entropy,
binary_cross_entropy_prime,
x_train,
y_train,
epochs=20,
learning_rate=0.1
)
# test
for x, y in zip(x_test, y_test):
output = predict(network, x)
print(f"pred: {np.argmax(output)}, true: {np.argmax(y)}")
Hết.